Building a computer from scratch is an exciting endeavor, and the motherboard is one of the most critical components you’ll need to choose carefully. The motherboard acts as the central hub of your PC, connecting all the essential parts like the CPU, RAM, storage, and graphics card. Selecting the right parts ensures your computer runs efficiently, making it ideal for enthusiasts, gamers, or industry professionals.
Whether you’re upgrading an older PC or building a new one, this guide will walk you through the key factors to consider when choosing, helping you make the right choice for your setup. Let’s explore the different types of motherboards, what features matter, and how to pick the best one for your computer.
Materials or Tools Needed for Choosing a Motherboard
Before diving into the motherboard selection process, make sure you have the following:
- Computer for research and specification comparison.
- List of compatible CPUs, RAM, and storage devices.
- Budget range to determine how much you are willing to spend.
- Compatibility check software to confirm your components work together (optional but useful).
Step-by-Step Instructions on How to Choose a Motherboard
Step 1: Determine the Socket Type for Your Processor
The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the brain of your computer, and it needs a motherboard with a compatible socket to function. Motherboards are designed to fit specific CPU types, such as Intel or AMD processors. For example, AMD’s latest processors use the AM5 socket, while Intel’s newer models use the LGA 1700 socket. Before purchasing, check your processor’s socket type and ensure the motherboard supports it.
Compatibility is key; a mismatch between your CPU and motherboard will render your system inoperable.
Step 2: Choose the Right Chipset for Your Needs
Each motherboard comes with a chipset, which determines the features and limitations. A chipset controls communication between the CPU, RAM, storage devices, and peripherals. For example, AMD’s B550m chipset supports PCIe 4.0 and overclocking, making it a good choice for mid-range builds. On the other hand, Intel’s Z-series chipsets are known for their overclocking potential and support for faster memory.
Pick a chipset based on the features you need, such as USB ports, PCIe lanes, and overclocking abilities.
Step 3: Determine the Form Factor of the Motherboard
Motherboards come in different sizes, known as form factors. The most common form factors are ATX, Micro-ATX, and Mini-ITX. The size you choose depends on your case and the amount of hardware you plan to install. For example, a Micro-ATX board like the Gigabyte B550m will offer fewer expansion slots but will fit in a smaller case. Meanwhile, ATX boards offer more slots for additional GPUs, storage drives, and peripherals but require a larger case.
Ensure the form factor fits your PC case and has enough room for your components.
Step 4: Check for Expansion Slots and Connectivity Options
A good motherboard should have enough expansion slots and ports for all your hardware and peripherals. For gaming or high-performance tasks, you’ll want a motherboard with multiple PCIe slots for installing multiple graphics cards or storage devices. Look for enough RAM slots, as well, so you can upgrade memory in the future.
Also, check for USB ports, Wi-Fi support, and M.2 slots for SSDs. These features will ensure you have flexibility as you upgrade or expand your PC later.
Step 5: Make Sure Your Motherboard Has Adequate Power and Cooling
Modern motherboards come with built-in features for power management and cooling. For example, MSI motherboards often include heatsinks and fan headers, which help keep the system cool during high-performance operations. Ensure it has enough fan headers to support your cooling setup and offers adequate power delivery for components like the CPU and GPU.
Proper cooling is crucial to ensure stability and longevity, especially if you’re overclocking.
Do’s and Don’ts When Choosing a Motherboard
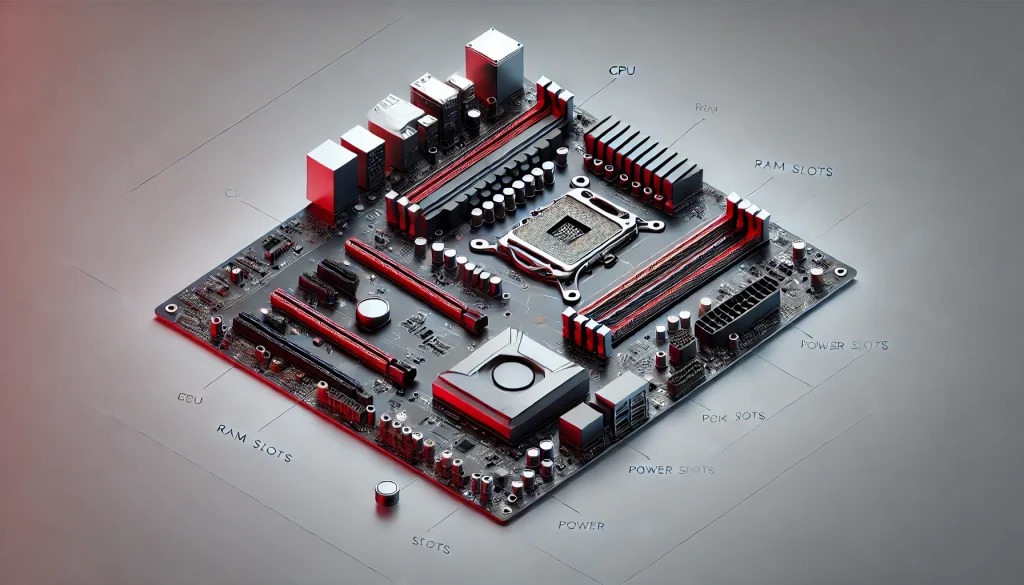
Do’s:
- Do consider future upgrades: Choose a motherboard that allows for future upgrades, like more RAM slots or PCIe expansion slots. This will save you from needing to replace the entire board when you want to upgrade your components.
- Do match your it with your CPU: Always verify that your motherboard and CPU are compatible. Look for the right socket type (e.g., AM5 for AMD or LGA 1200 for Intel).
- Do invest in a quality power supply: Your motherboard needs stable power delivery, especially when running high-end CPUs or GPUs. A good power supply will ensure your system runs reliably.
- Do check for sufficient USB ports and storage options: Ensure your motherboard has enough USB ports and slots for storage devices, like M.2 drives or traditional SATA drives.
Don’ts:
- Don’t go overboard with features you won’t use: Avoid paying extra for features like multi-GPU support or extreme overclocking capabilities if you don’t need them.
- Don’t neglect the form factor: Choosing the wrong form factor might limit your expansion options or make it difficult to fit the motherboard into your case.
- Don’t skimp on the chipset: Cheaper chipsets may lack essential features like PCIe 4.0 support or high-speed USB ports, which are important for gaming or professional applications.
Conclusion
Selecting the right motherboard is crucial for a successful PC build, and the process involves considering compatibility, features, and future-proofing. By determining the correct socket, chipset, and form factor, you can ensure your system runs smoothly and meets your needs. Whether you’re building a gaming rig or a professional workstation, this guide should help you make an informed decision and choose the perfect for your build.
FAQ
What is the most important factor when choosing a motherboard?
The most critical factor is compatibility with your CPU and the required socket type. Without the correct socket, the CPU won’t work with the motherboard.
Is it better to buy a more expensive motherboard?
Not necessarily. The best motherboard is one that meets your needs, not necessarily the most expensive one. Expensive motherboards have additional features, but many users won’t need those extras.
Can I upgrade my CPU without changing the motherboard?
This depends on the motherboard and its supported socket and chipset. Some motherboards support multiple generations of CPUs, while others may require a replacement when upgrading.
Resources:
- How-To Geek. How to Choose a Motherboard for Your PC: What to Look For.
- Newegg. How to Choose a Motherboard.
- PCMag. The Best Motherboards of 2024.
- The CPU Guide. Choose the Right Motherboard for Your PC Build.
- Tom’s Hardware. Motherboard Buying Guide: How to Pick the Perfect Board.

Brijesh Gohil is the founder of Tech Brij, A popular Tech Blog which is focused on Tech tips & Buying Guides. You can follow him on Facebook, Twitter, Google + & LinkedIn.